
MCAT-TEST Exam Questions & Answers
Exam Code: MCAT-TEST
Exam Name: Medical College Admission Test: Verbal Reasoning, Biological Sciences, Physical Sciences, Writing Sample
Updated: Apr 30, 2024
Q&As: 812
At Passcerty.com, we pride ourselves on the comprehensive nature of our MCAT-TEST exam dumps, designed meticulously to encompass all key topics and nuances you might encounter during the real examination. Regular updates are a cornerstone of our service, ensuring that our dedicated users always have their hands on the most recent and relevant Q&A dumps. Behind every meticulously curated question and answer lies the hard work of our seasoned team of experts, who bring years of experience and knowledge into crafting these premium materials. And while we are invested in offering top-notch content, we also believe in empowering our community. As a token of our commitment to your success, we're delighted to offer a substantial portion of our resources for free practice. We invite you to make the most of the following content, and wish you every success in your endeavors.
Download Free MCAT MCAT-TEST Demo
Experience Passcerty.com exam material in PDF version.
Simply submit your e-mail address below to get started with our PDF real exam demo of your MCAT MCAT-TEST exam.
![]() Instant download
Instant download
![]() Latest update demo according to real exam
Latest update demo according to real exam
* Our demo shows only a few questions from your selected exam for evaluating purposes
Free MCAT MCAT-TEST Dumps
Practice These Free Questions and Answers to Pass the MCAT Certifications Exam
Although nihilism is commonly defined as a form of extremist political thought, the term has a broader meaning. Nihilism is in fact a complex intellectual stance with venerable roots in the history of ideas, which forms the theoretical basis for many positive assertions of modern thought. Its essence is the systematic negation of all perceptual orders and assumptions. A complete view must account for the influence of two historical crosscurrents: philosophical skepticism about the ultimacy of any truth, and the mystical quest for that same pure truth. These are united by their categorical rejection of the "known". The outstanding representative of the former current, David Hume (1711?776), maintained that external reality is unknowable, since sense impressions are actually part of the contents of the mind. Their presumed correspondence to external "things" cannot be verified, since it can be checked only by other sense impressions. Hume further asserts that all abstract conceptions turn out, on examination, to be generalizations from sense impressions. He concludes that even such an apparently objective phenomenon as a cause-and-effect relationship between events may be no more than a subjective fabrication of the observer. Stanley Rosen notes: "Hume terminates in skepticism because he finds nothing within the subject but individual impressions and ideas". For mystics of every faith, the "experience of nothingness" is the goal of spiritual practice. Buddhist meditation techniques involve the systematic negation of all spiritual and intellectual constructs to make way for the apprehension of pure truth. St. John of the Cross similarly rejected every physical and mental symbolization of God as illusory. St. John's spiritual legacy is, as Michael Novak puts it, "the constant return to inner solitude, an unbroken awareness of the emptiness at the heart of consciousness. It is a harsh refusal to allow idols to be placed in the sanctuary. It requires also a scorching gaze upon all the bureaucracies, institutions, manipulators, and hucksters who employ technology and its supposed realities to bewitch and bedazzle the psyche". Novak's interpretation points to the way these philosophical and mystical traditions prepared the ground for the political nihilism of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The rejection of existing social institutions and their claims to authority is in the most basic sense made possible by Humean skepticism. The political nihilism of the Russian intelligentsia combined this radical skepticism with a near mystical faith in the power of a new beginning. Hence, their desire to destroy becomes a revolutionary affirmation; in the words of Stanley Rosen, "Nihilism is an attempt to overcome or repudiate the past on behalf of an unknown and unknowable, yet hoped-for, future." This fusion of skepticism and mystical re-creation can be traced in contemporary thought, for example as an element in the counterculture of the 1960s.
Which of the following provides the best continuation for the final paragraph of the passage?
A. Thus, the negative effects of nihilism are still being felt.
B. Classical nihilism has thus been superseded by a new and unrelated type.
C. The revolutionaries of that time did, after all, reject society and hope for something better.
D. The study of nihilism, then, belongs to the past rather than to the present.
According to Piaget, which is the first stage of cognitive development?
A. sensorimotor
B. formal operational
C. concrete operational
D. preoperational
The process by which individuals decide and choose to seek assistance for health or mental health problems is called help-seeking. Table 1 displays the percentage of American Indian/Alaska Native and non-Hispanic White adults who received mental health or counseling treatment in 2008
Help-seeking is a complex process and individuals will choose to obtain treatment for a variety of reasons. One of the strongest individual-related help-seeking predictors amounts to perceiving the need to do so. Other individual-related factors are the educational and the socioeconomic status. There may also be systematic factors that prevent people from doing so, such as general mistrust of health, mental health, and social service institutions, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. It has been speculated that some of the mistrust stems from research studies, sponsored by medical establishments, where racial and ethnic minorities express concerns of being recruited for the purpose of serving as guinea pigs. Focus groups with African Americans and Chinese immigrants confirmed this anxiety and fear.
Thus, cultural factors also play a role in the help-seeking process. Western cultural norms about medicine are premised on norms of individualism. However, individuals from other cultures and racial and ethnic minority groups tend to be both more collectivistic and fatalist. Disease, both medical and mental, is believed to occur because of fate. It is not something where one should spend much time and effort fighting; the needs of the family and even of the extended family are to come first.
Table 1 Access to health care: Percentage of adults who received mental health treatment or counseling in the past year, 2008
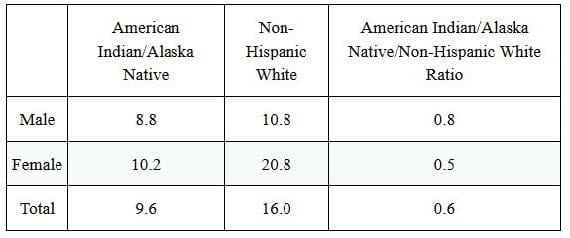
Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,"Mental Health and American Indians/ Alaska Natives"
What variables will a researcher interested in investigating the relationship between the "Big Five" personality traits and help-seeking behaviors include in the study?
A. Traditional, egalitarian, patriarchal, matriarchal, and androgynous
B. Overgeneralizations, polarized thinking, personalization, catastrophizing, and blaming
C. Neuroticism, extraversion, openness, agreeableness, and conscientiousness
D. Persona, shadow, anima, animus, and self
The equation for Ampere law is:
A. µoI = Br
B. µoI = Br2
C. µoI = B2r
D. µoI = B2r2
For a very weak base, the pKb of a solution would likely be:
A. Equal to the pOH
B. Higher than the pOH
C. Lower than the pOH
D. Near 7 at 25篊
Viewing Page 2 of 3 pages. Download PDF or Software version with 812 questions

