
CCRA Exam Questions & Answers
Exam Code: CCRA
Exam Name: Certified Credit Research Analyst
Updated: Apr 19, 2024
Q&As: 84
At Passcerty.com, we pride ourselves on the comprehensive nature of our CCRA exam dumps, designed meticulously to encompass all key topics and nuances you might encounter during the real examination. Regular updates are a cornerstone of our service, ensuring that our dedicated users always have their hands on the most recent and relevant Q&A dumps. Behind every meticulously curated question and answer lies the hard work of our seasoned team of experts, who bring years of experience and knowledge into crafting these premium materials. And while we are invested in offering top-notch content, we also believe in empowering our community. As a token of our commitment to your success, we're delighted to offer a substantial portion of our resources for free practice. We invite you to make the most of the following content, and wish you every success in your endeavors.
Download Free AIWMI CCRA Demo
Experience Passcerty.com exam material in PDF version.
Simply submit your e-mail address below to get started with our PDF real exam demo of your AIWMI CCRA exam.
![]() Instant download
Instant download
![]() Latest update demo according to real exam
Latest update demo according to real exam
* Our demo shows only a few questions from your selected exam for evaluating purposes
Free AIWMI CCRA Dumps
Practice These Free Questions and Answers to Pass the CCRA Exam
Following is information related banks:
Auckland Ltd is a public sector bank operating with about 120 branches across India. The bank has been
in business since 1971 and has about 40% branches in rural areas and about 75% of all branches are in Western India. On the basis of the size, Auckland Ltd will be ranked at number 31 amongst 40 banks in India. Although top management has appointment period of 5 years, generally they retire on ach sieving age of 60 years with an average tenure of only 2 years at the top job.
Profit and Loss Account
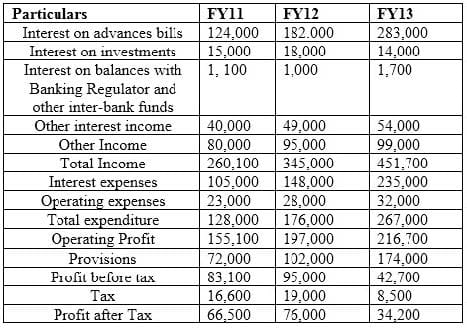
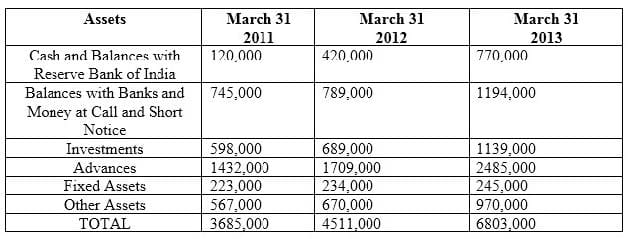
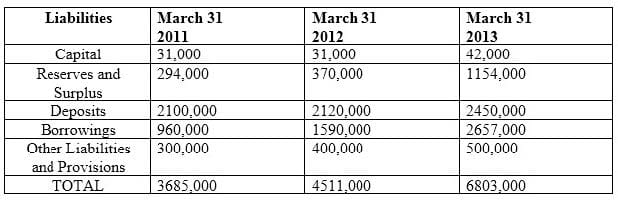
Balance Sheet
The rating wise break-up of assets for FY11 is as follows:
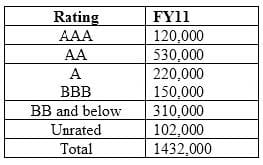
During which year amongst the three, was the overall financial profile of bank most string?
A. No change in three years
B. FY13
C. FY11
D. FY12
Satish Dhawan, a veteran fixed income trader is conducting interviews for the post of a junior fixed income trader. He interviewed four candidates Adam, Balkrishnan, Catherine and Deepak and following are the answers to his questions. Q-1: Tell something about Option Adjusted Spread
Adam: OAS is applicable only to bond which do not have any options attached to it. It is for the plain bonds.
Balkishna: In bonds with embedded options, AS reflects not only the credit risk but also reflects prepayment risk over and above the benchmark.
Catherine: Sincespreads are calculated to know the level of credit risk in the bound, OAS is difference between in the Z spread and price of a call option for a callable bond.
Deepark: For callable bond OAS will be lower than Z Spread.
Q-2: This is a spread that must be added to the benchmark zero rate curve in a parallel shift so that the sum of the risky bond's discounted cash flows equals its current market price. Which Spread I am talking about?
Adam: Z Spread
Balkrishna: Nominal Spread Catherine: Option Adjusted Spread Deepark: Asset Swap Spread
Q-3: What do you know about Interpolated spread and yield spread?
Adam: Yield spread is the difference between the YTM of a risky bond and the YTM of an on-the-run treasury benchmark bond whose maturity is closest, but not identical to that of risky bond. Interpolated spread is the spread between the YTM of risky bond and the YTM of same maturity treasury benchmark, which is interpolated from the two nearest on-the-run treasury securities.
Balkrishna: Interpolated spread is preferred to yield spread because the latter has the maturity mismatch, which leads to error if the yield curve is not flat and the benchmark security changes over time, leading to inconsistency.
Catherine: Interpolated spread takes account the shape of the benchmark yield curve and therefore better than yield spread.
Deepak: Both Interpolated Spread and Yield Spread rely on YTM which suffers from drawbacks and inconsistencies such as the assumption of flat yield curve and reinvestment at YTM itself.
Then Satish gave following information related to the benchmark YTMs:
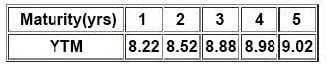
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 4.75 year(s). Its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds to YTM of 9.22%. Compute Interpolated Spread from the information provided in the vignette:
A. 0.20%
B. 0.21%
C. 0.24%
D. 0.22%
A coupon bond is trading at 110% of the USD 1000 par value. If the last interest payment was made one month ago and the coupon rate is 12%, the accrued interest on this bond is_______
A. 110
B. 100
C. 120
D. 10
Stand by letter of credits are typically taken as credit enhancement for___________
A. Commercial Paper
B. Long term Bond issues
C. Long term debenture issues
D. Bank debt
Provisioning Coverage Ratio (PCR) is essentially the ratio of provisioning to ______ and indicates the extent of funds a bank has kept aside to cover loan losses.
A. total loan portfolio
B. gross non-performing assets
C. total assets
Viewing Page 1 of 3 pages. Download PDF or Software version with 84 questions

